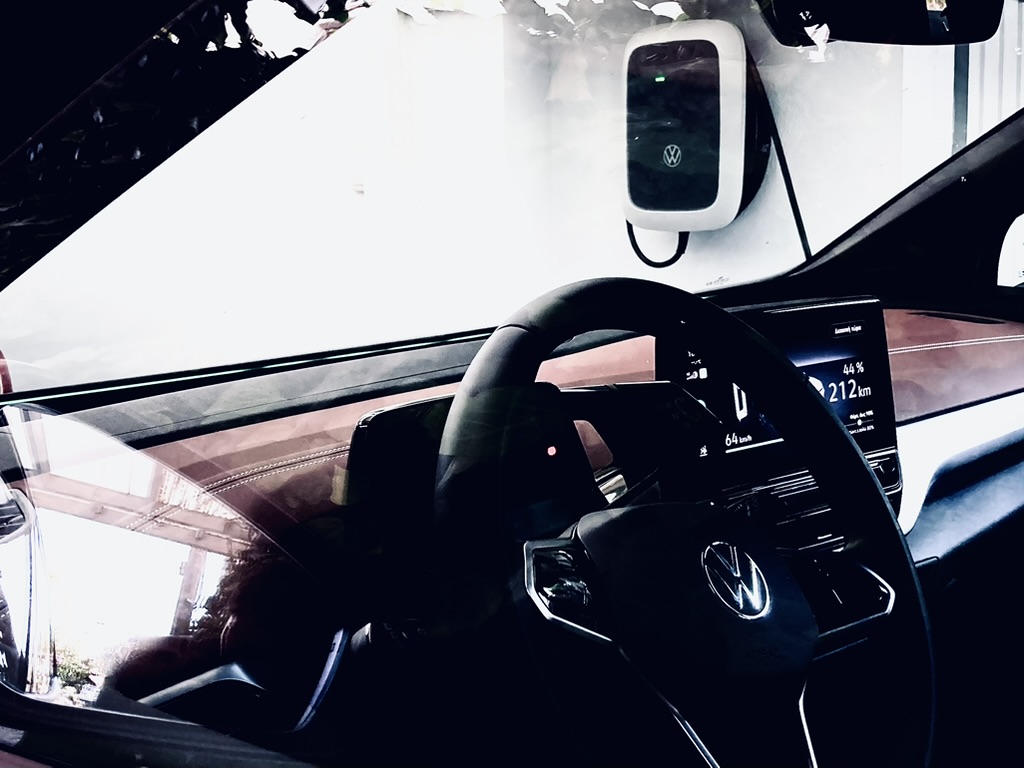
The charging speed of an EV is determined by 4 factors:
- Your power utility contract
- Maximum charging speed of the electric vehicle
- Charging station
- Charging cable
1. Your power utility contract
Your power utility company as well as the wiring / fuses / CBs of your electrical system, as well as the installed electrical appliances, e.g. lights, A/Cs, water heaters, kitchen appliances, pumps, elevators, etc. determines the maximum available power for your charging station.
3-phase vs single phase power supply
- Your power supply is either three-phase or single-phase
- All EVs can be charged from either a three-phase or a single-phase supply
- Some electric vehicles will charge faster from a three-phase power supply than a single-phase power supply
To take advantage of the 3-phase supply you must:
- Your EV must support 3-phase charging. Jump to: Maximum charging speed of the EV
- Your charging station must support 3-phase charging. Jump to: Charging station
- If you are using a charging station without a tethered cable, the cable must support 3-phase charging. Jump to: Charging cable
To learn what your power supply you have, you can contact your electrician or power utility company. Alternatively, the Virtual Survey service can help you identify the power supply and determine the ideal charging solution.
2. Maximum charging speed of the electric vehicle
The on-board charger of the EV determines the maximum charging speed supported by the vehicle.
Please note that some vehicle manufacturers offer the same model with different on-board chargers.
Some examples of vehicles with different on-board chargers:
- The electric Peugeot models are sold with 7.4 kW on-board charger as standard equipment, while the 11 kW on-board charger is offered as an option.
- smart fortwo in its standard version has a 4.6 kW on-board charger, while you can optionally order the vehicle with a 22 kW on-board charger option.
- The early BMW and Jaguar models were equipped with a 7,4 kW on-board charger, whereas later models come equipped with a 11 kW on-board charger.
How to identify which on-board charger does your EV have:
- Based on the your vehicle specification
- By examining the charging port of your vehicle
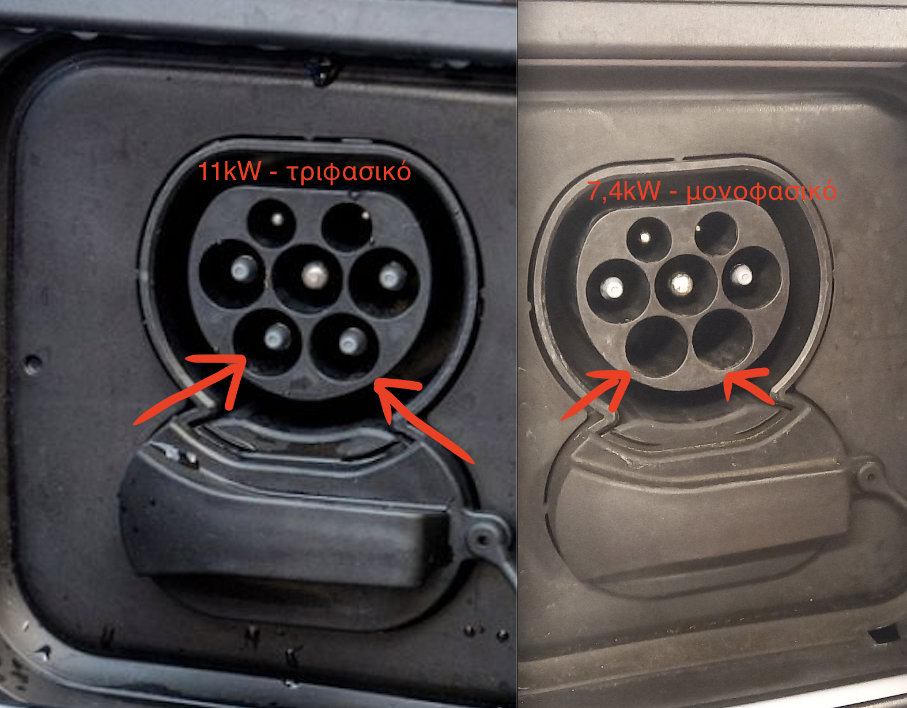

Example of a three-phase version (11kW) and a single-phase version (7.4kW) charging port of the same vehicle (BMW i3).
*The above photos are indicative and do not constitute a definitive method of determining if your vehicle is single-phase or three-phase. Some single-phase vehicles may have ports similar to three-phase port, however, if your vehicle socket resembles a single-phase port (without the two contacts of the bottom row), your vehicle is single-phase.
Important:
- The on-board charger is an integral part of your vehicle and can not be replaced/retrofitted after ordering the vehicle.
- Some vehicles support rapid charging (Level 3) which uses direct current (DC) and can charge at speeds of 50 kW and higher. These charging stations use a different technology (and plugs/ports) and are primarily implemented on highways.
3. Charging stations
The charging station you use can determine the charging speed:
- Level 1 chargers that connect to a residential wall socket can charge your vehicle only at single phase speeds ranging from 1.7 to 2.3 kW.
- Level 2 charging stations use utilize a single-phase or three-phase power allowing speeds up to 22 kW.
- Level 3 charging stations use direct current (DC) and can recharge an EVs for 100km of range in about 20 minutes.
4. Charging cable
If you use a charging station without a tethered cable, the cable may limit your charging speed.
Tips for choosing the ideal charging cable for maximum charging speed:
- If your vehicle, power supply and charging station support all three-phase charging, using the three-phase cable can triple the charging speed.
- Single-phase charging usually supports a higher current (32A as opposed to 16A) given that such currents can be supported by your power supply and charging station.
- It is safe to use any certified Level 2 charging cable, even if it is not the ideal choice for your particular vehicle or charging station.